In the global pursuit of sustainable solutions, paper packaging has emerged as a champion. Once a simple utilitarian tool, it has evolved into a complex and dynamic component of modern supply chains. This evolution has been driven by changing consumer expectations, environmental urgency, technological advancements, and regulatory pressures. This article explores the historical transformation, material innovations, and the future direction of paper-based packaging.
From Wood Pulp to Kraft: The Origins of Paper Packaging
The journey of paper packaging began with the discovery and mass production of wood pulp-based paper in the 19th century. Initially used for wrapping and simple containment, the material was inexpensive, lightweight, and relatively easy to manufacture. By the early 20th century, kraft paper—named after the German word for strength—became the dominant form for packaging due to its durability.

Key Characteristics:
- Derived from softwood trees using the kraft process.
- Strong and tear-resistant, making it ideal for industrial use.
- Fully biodegradable and recyclable.
While functional, this early paper packaging lacked barrier properties—such as water and grease resistance—limiting its use for food and perishables.
Coatings and Composites: The Plastic Era Begins
Post-World War II, the world saw a boom in industrial innovation, and packaging was no exception. To address the limitations of plain paper, manufacturers began coating and laminating paper with other materials, especially plastics and aluminum.

Common Materials Introduced:
- Polyethylene (PE): Provided waterproofing for cartons and wrappers.
- Aluminum foil: Offered excellent oxygen and light barriers, critical for preserving food.
- Wax coatings: Widely used in fast food and bakery applications.
This era saw the rise of multi-material packaging, which improved product protection and shelf life. However, it came at a cost: recyclability. The fusion of different materials made separation and recycling extremely difficult, a challenge that still affects the industry today.
Recycled Paper and Lightweighting: The Green Awakening
By the 1990s, environmental concerns started gaining mainstream traction. Landfills were overflowing with plastic-laminated packaging, and consumers became more aware of ecological footprints. In response, manufacturers began incorporating recycled content and exploring ways to lightweight packaging without compromising performance.
Innovations During This Era:
- Increased use of post-consumer recycled (PCR) fibers.
- Transition to soy-based inks and water-based adhesives.
- Reduction in material thickness (lightweighting) to cut waste and cost.
Regulatory frameworks such as Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) and green certifications (e.g., FSC and PEFC) began shaping the way paper packaging was designed, sourced, and disposed of.
Functional Paper: Engineering Performance Without Plastic
In the 2010s, sustainability became more than just a corporate checkbox—it became a consumer demand and brand differentiator. This gave rise to functional papers engineered to replace plastic in applications where it once seemed indispensable.
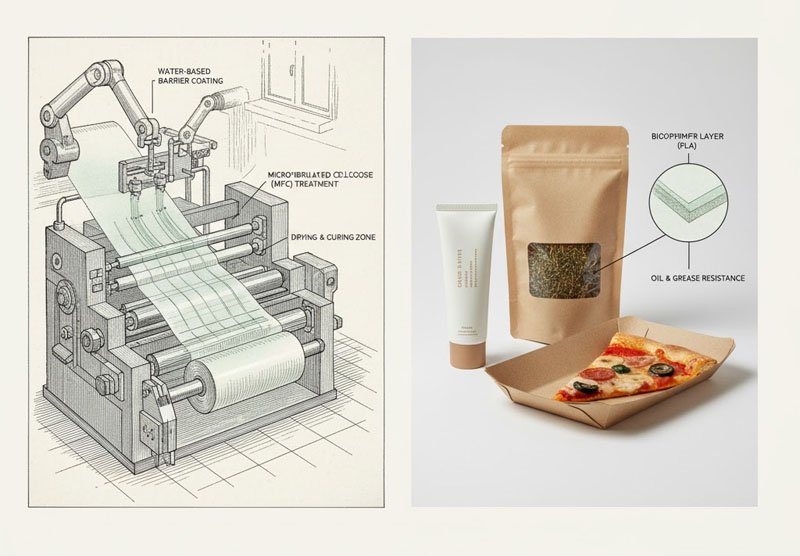

Breakthrough Materials:
- Water-based barrier coatings: Provide resistance to oil, grease, and moisture.
- Biopolymers like PLA (polylactic acid): Compostable alternatives for plastic film layers.
- Microfibrillated cellulose (MFC): Enhances strength and creates natural barriers.
Innovative brands and startups started developing mono-material packaging that could be easily recycled in existing paper streams. Companies like Nestlé, Unilever, and L’Oréal began piloting paper-based tubes, pouches, and trays that delivered performance without compromising sustainability.
The Rise of Molded Fiber and 3D Paper Forms
As e-commerce and food delivery grew exponentially in the late 2010s, so did the demand for plastic-free rigid packaging. Molded fiber technology—traditionally used for egg cartons—was reimagined to create custom-shaped, durable, and sustainable packaging.
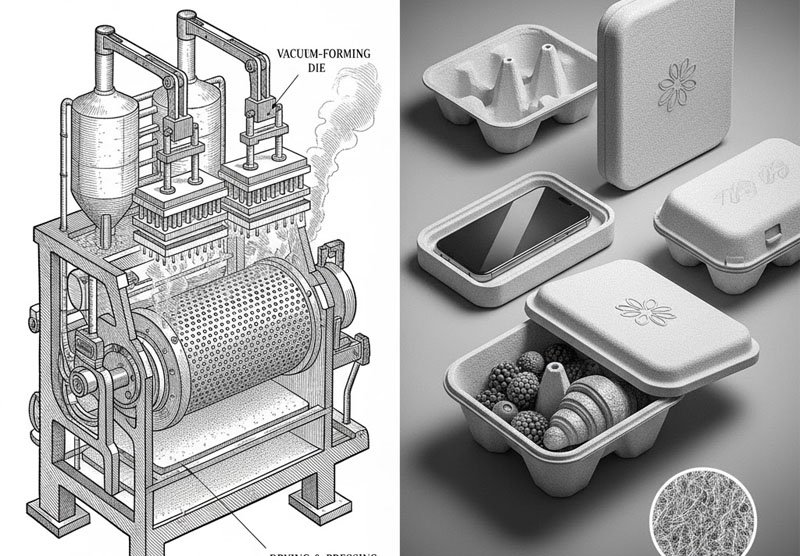
Applications of Molded Fiber:
- Protective packaging for electronics and cosmetics.
- Foodservice containers replacing foam and plastic.
- Luxury packaging with embossed logos and unique textures.
This shift was driven by both plastic bans and brand storytelling. Packaging was no longer just a container; it became a tactile extension of a brand’s values.
Intelligent and Circular: The Future of Paper Packaging
Looking forward, the future of paper packaging lies at the intersection of intelligent design and the circular economy. Material scientists, designers, and policymakers are working together to create solutions that go beyond recyclability to regenerativity.

Emerging Trends:
- Smart coatings: Use of nanotechnology and bio-based barriers for food safety and freshness.
- Digital watermarks: Invisible codes on packaging for better sorting in recycling facilities (e.g., HolyGrail 2.0).
- Fiber-based bottles and caps: Replacing entire plastic systems with biodegradable counterparts.
- Reusability and refill systems: Paper designed for multiple uses with durable finishes.
Additionally, carbon footprint tracking, traceability, and material transparency will become crucial components of future packaging systems. Governments are pushing for closed-loop systems, where every material reenters the supply chain instead of becoming waste.
Conclusion
The evolution of materials in paper packaging is a remarkable testament to human ingenuity adapting to environmental necessity. From simple kraft paper to bio-engineered smart materials, each phase has been a response to a unique set of challenges—performance, cost, convenience, and most recently, sustainability.
However, the journey is far from over. As consumer expectations grow and climate urgency increases, the paper packaging industry must continue to innovate responsibly. This means designing with end-of-life in mind, embracing mono-material simplicity, and investing in technologies that restore rather than deplete the planet.
The packaging of tomorrow is not just about holding a product—it’s about holding a promise.







